Your cart is empty
Start Shopping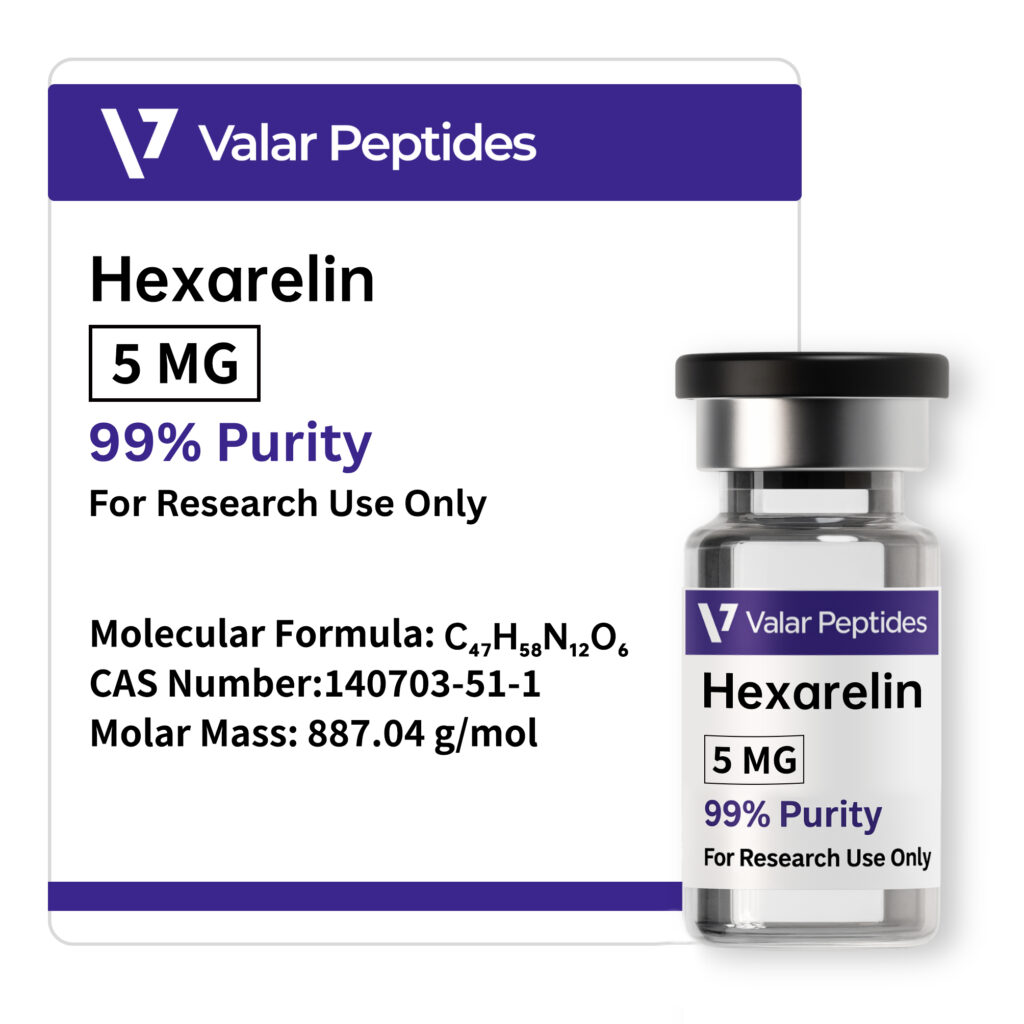
$42.00
This material is sold for laboratory research use only. Terms of sale apply. Not for human consumption, nor medical, veterinary, or household uses. Please familiarize yourself with our Terms & Conditions prior to ordering.
| Molecular Formula | C₄₇H₅₈N₁₂O₆ |
| CAS Number | 140703-51-1 |
| Molar Mass | 887.04 g/mol |
| Amino Acid Sequence | His-D-2-methyl-Trp-Ala-Trp-D-Phe-Lys-NH2 |
| PubChem CID | 6918297 |
| Primary Research Area |
Growth Hormone Secretagogue Growth Hormone Deficiency Cardioprotection Congestive Heart Failure Myocardial Infarction Cardiac Remodeling Neuroprotection Oxidative Stress Inflammation Muscle Growth Adipose Tissue Reduction GHSR-1a Agonism CD36 Receptor Activation |
| Purity | >99% |
| Research Summary | Description |
|---|---|
| The cardiovascular action of hexarelin |
Summary: This concise review article summarizes the evidence for the direct cardiovascular actions of hexarelin. It highlights that beyond its role as a GHSR-1a agonist, hexarelin exerts significant cardioprotective effects, including the inhibition of cardiomyocyte apoptosis (programmed cell death of heart muscle cells), reduction of cardiac fibrosis, and improvement of cardiac function in models of myocardial infarction and heart failure. The review emphasizes that these effects are partly mediated by GHSR-1a but largely by activation of the CD36 receptor, a multifunctional B-type scavenger receptor identified as a specific cardiac receptor for hexarelin. Citation: Zhang, W., & Chen, J. (2014). The cardiovascular action of hexarelin. Endocrine, 47(2), 346–352. |
| Protective effects of Hexarelin and JMV2894 in a human neuroblastoma cell line expressing the SOD1-G93A mutated protein |
Summary: This in vitro study investigated the neuroprotective potential of hexarelin in human neuroblastoma cells overexpressing the SOD1-G93A mutated protein, a model for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). The study found that hexarelin effectively antagonized hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage to these cells. It improved cell viability, reduced nitrite release (a marker of oxidative stress), and restored normal cell morphologies. Mechanistically, hexarelin reduced caspase-3 activation (an apoptotic enzyme) and modulated the expression of BCL-2 family proteins, suggesting anti-apoptotic effects. It also influenced MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, which are crucial for cell survival. Citation: Vittorelli, D., Giustizieri, M. L., De Stefano, S., Costantini, R., Brizzi, A., Manno, R., ... & Fuso, A. (2023). Protective Effects of Hexarelin and JMV2894 in a Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line Expressing the SOD1-G93A Mutated Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 993. |
| Hexarelin modulates lung mechanics, inflammation, and fibrosis in acute lung injury |
Summary: This study investigated the effects of hexarelin in a murine model of HCl-induced acute lung injury (ALI), a condition that can lead to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and lung fibrosis. Hexarelin treatment induced a significant improvement in lung compliance and reduced the total number of immune cells and neutrophil recruitment in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid within 24 hours of injury. It also demonstrated an ability to blunt lung remodeling processes and fibrotic development. The findings suggest that hexarelin can inhibit the early phase of the inflammatory response, thereby preventing subsequent fibrotic changes. Citation: Toscano, M., Cataldi, M., D'Adamo, E., Vitiello, G., Zaccaria, C., Vetrone, S., ... & Gualillo, O. (2021). Hexarelin modulates lung mechanics, inflammation, and fibrosis in acute lung injury. Drug Target Insights, 15, 26–33. |
| Growth hormone-independent cardioprotective effects of hexarelin in the rat |
Summary: This study explored whether hexarelin's cardioprotective effects were independent of its GH-releasing activity. Using hypophysectomized rats (which lack a pituitary gland and thus cannot produce GH), the researchers found that hexarelin treatment prevented the exacerbation of ischemia-reperfusion damage in the heart. Hexarelin prevented increases in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, coronary perfusion pressure, and reversed the fall in prostacyclin release. Importantly, a control GH-releasing peptide (EP 51389) that does not bind to the heart, but also stimulates GH, was ineffective in this model. Citation: Luciani, S., De Gennaro Colonna, V., & Deghenghi, R. (1999). Growth hormone-independent cardioprotective effects of hexarelin in the rat. Endocrinology, 140(9), 4024–4029. |
Summary: This concise review article summarizes the evidence for the direct cardiovascular actions of hexarelin. It highlights that beyond its role as a GHSR-1a agonist, hexarelin exerts significant cardioprotective effects, including the inhibition of cardiomyocyte apoptosis (programmed cell death of heart muscle cells), reduction of cardiac fibrosis, and improvement of cardiac function in models of myocardial infarction and heart failure. The review emphasizes that these effects are partly mediated by GHSR-1a but largely by activation of the CD36 receptor, a multifunctional B-type scavenger receptor identified as a specific cardiac receptor for hexarelin.
Citation:
Zhang, W., & Chen, J. (2014). The cardiovascular action of hexarelin. Endocrine, 47(2), 346–352.
Summary: This in vitro study investigated the neuroprotective potential of hexarelin in human neuroblastoma cells overexpressing the SOD1-G93A mutated protein, a model for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). The study found that hexarelin effectively antagonized hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage to these cells. It improved cell viability, reduced nitrite release (a marker of oxidative stress), and restored normal cell morphologies. Mechanistically, hexarelin reduced caspase-3 activation (an apoptotic enzyme) and modulated the expression of BCL-2 family proteins, suggesting anti-apoptotic effects. It also influenced MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, which are crucial for cell survival.
Citation:
Vittorelli, D., Giustizieri, M. L., De Stefano, S., Costantini, R., Brizzi, A., Manno, R., ... & Fuso, A. (2023). Protective Effects of Hexarelin and JMV2894 in a Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line Expressing the SOD1-G93A Mutated Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 993.
Summary: This study investigated the effects of hexarelin in a murine model of HCl-induced acute lung injury (ALI), a condition that can lead to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and lung fibrosis. Hexarelin treatment induced a significant improvement in lung compliance and reduced the total number of immune cells and neutrophil recruitment in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid within 24 hours of injury. It also demonstrated an ability to blunt lung remodeling processes and fibrotic development. The findings suggest that hexarelin can inhibit the early phase of the inflammatory response, thereby preventing subsequent fibrotic changes.
Citation:
Toscano, M., Cataldi, M., D'Adamo, E., Vitiello, G., Zaccaria, C., Vetrone, S., ... & Gualillo, O. (2021). Hexarelin modulates lung mechanics, inflammation, and fibrosis in acute lung injury. Drug Target Insights, 15, 26–33.
Summary: This study explored whether hexarelin's cardioprotective effects were independent of its GH-releasing activity. Using hypophysectomized rats (which lack a pituitary gland and thus cannot produce GH), the researchers found that hexarelin treatment prevented the exacerbation of ischemia-reperfusion damage in the heart. Hexarelin prevented increases in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, coronary perfusion pressure, and reversed the fall in prostacyclin release. Importantly, a control GH-releasing peptide (EP 51389) that does not bind to the heart, but also stimulates GH, was ineffective in this model.
Citation:
Luciani, S., De Gennaro Colonna, V., & Deghenghi, R. (1999). Growth hormone-independent cardioprotective effects of hexarelin in the rat. Endocrinology, 140(9), 4024–4029.
Your cart is empty
Start Shopping